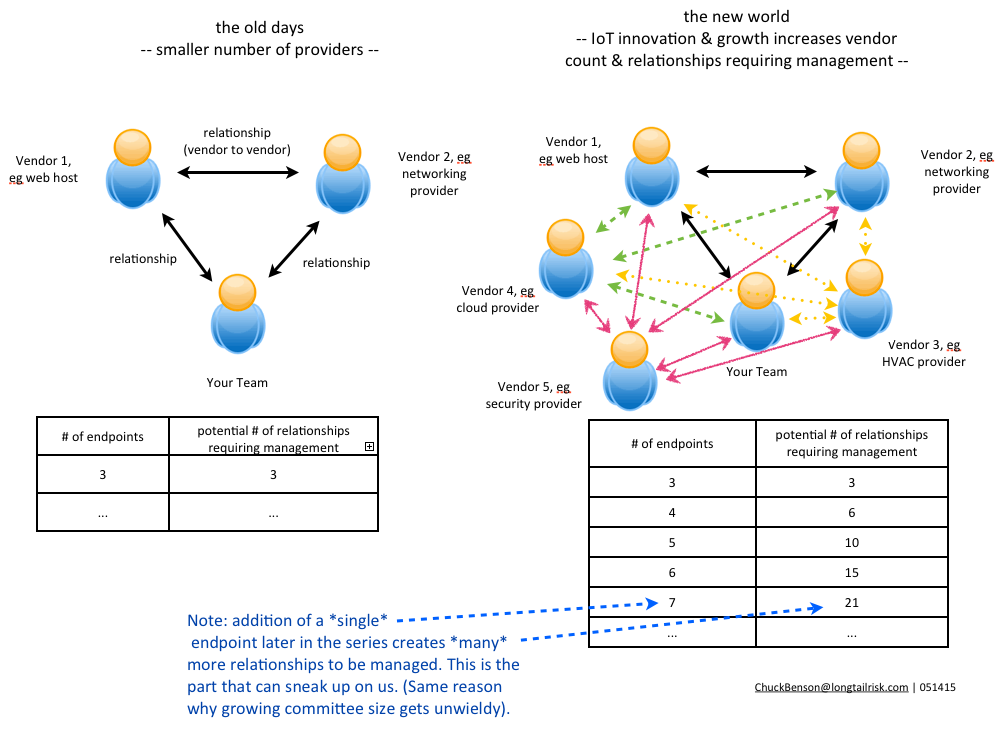
The vendor count for IoT systems that a company or organization manages will only increase in the coming months and years and it will possibly increase substantially. Some of this will be from traditional systems like HVAC that have been in the space longer than most and are maturing and extending their IoT development and deployment. New growth in an organizations’s vendor count will be from vendors with brand new products and service lines made possible by IoT innovation and expansion. Many of the benefits of IoT will be from products and services from different vendors that interact and exchange information with each other such as an IoT implementation leveraging the cloud. Regardless of the source, the number of IoT vendors that an organization has will grow.
This increased IoT system vendor count is not a bad thing in its own right. However, a somewhat insidious effect is that the number of relationships to be managed (or not managed) will grow even faster than the increasing vendor count itself.
Relationships have friction
Every relationship has friction or loss from an idealized state. Nature has plenty of examples — pressure loss in a pipe, channel capacity in information theory, marriage, and heat engine efficiency established nearly 200 years ago by Sadi Carnot. Carl Von Clausewitz famously established the concept of friction in war in his book On War in which he sometimes evokes the image of two wrestlers in a relationship.
Relationships between business customer and their vendors have friction too — from day-to-day relationship management overhead such as communication planning and contract management to more challenging aspects such as expectation alignment/misalignment and resource allocation problems.
Friction in a business customer-vendor relationship (unavoidable to some degree) means less information gets communicated than expected, similar to Shannon’s observations on information exchange. And similar to limits expressed with Carnot’s engine efficiency, less work gets done in practice than in the idealized state. Particularly for the former, a reduction in expected information exchange, by definition, increases uncertainty. Further, friction in a network of relationships can manifest itself in yet even more uncertainty. Less work gets done than is expected and the state of things is unclear.
With a growing network of nodes (IoT vendors in this case), the even faster growing number of relationships, and the friction that naturally exists between them, our business environments are becoming increasingly complex and accompanied with increased uncertainty. Vendor management and its associated risk, in the traditional sense, have left the building.
Sans organizational IoT strategy, IoT vendors will naturally optimize for themselves
While a strategy around IoT deployment and IoT vendor management can be difficult to devise and establish given the complexity and relative newness of the phenomenon, we have to acknowledge that vendors/providers will naturally optimize for themselves if we don’t have an IoT implementation strategy for our organizations.
This is not an easy thing. We really don’t know what is going to happen next in IoT innovation, so how do we establish strategy? Also, the strategy might cost something in terms of technical framework and staffing — and that is particularly hard to sell internally. However, without some form of an IoT system implementation strategy, each individual provider will offer a product or service line implementation that’s best for them. They won’t be managing the greater good of our organization. This is not evil, it’s natural in our market economy — but we as business consumers need to be aware of this.
Similar to the concept of building a socket in the last post, in establishing a policy or framework for IoT vendor relationships, some IoT vendor considerations might include:
- Are there standard frameworks that can be deployed to support requirements from multiple different IoT vendors? For example, does every vendor need their own dedicated, staffed, and managed database? If individual vendors demand dedicated support frameworks/infrastructure, are they willing to pay for it or otherwise subsidize it?
- Does your vendor offer a VM (virtual machine) image that works in your data center or with your cloud provider? Do they offer a service that helps integrate their VM image into your data center or cloud environment?
- Are there protocols that can be leveraged across multiple different vendors? Does the vendor in consideration participate in open-source protocols? For example, for managing trust, Trusted Computing Group has extended some of their efforts in an open source trust platform to the IoT space.
- Does the vendor provide a mechanism to help you manage them for performance? If so, the vendor acknowledges the additional complexity that managing many IoT systems brings and offers to help you review and manage performance.
While an IoT framework or policy at this stage is almost guaranteed to be imperfect, incomplete, and ephemeral, the cost of not having one puts your organization at every IoT system provider’s whim. And that cost is probably much higher.